![]()
Lecture Topics:
![]()
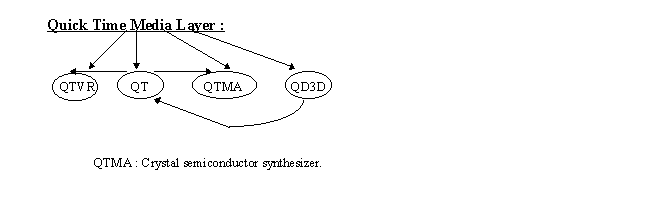
Quick Time Media Layer :
Odd and Even functions :
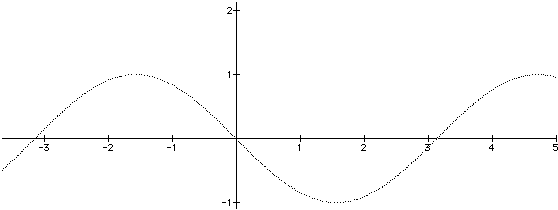
f(-x) = -f(x) => Odd function
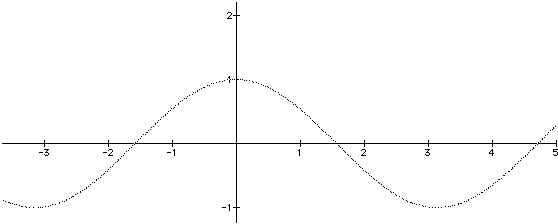
f(-x) = f(x) => Even function
Sin(-x) = -Sin(x) => Odd function.
Cos(-x) = Cos(x) => Even function.
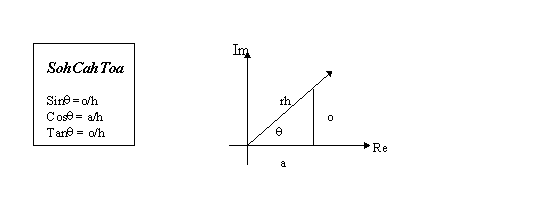
The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
Let x(n) be the sampled waveform :
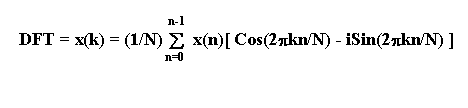
k = frequency index
f = frequency
fs = sample rate
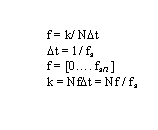
ie, for Audio CD's
fs = 44.4 KHz
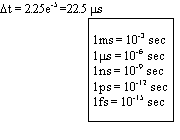
Note : DFP summation is performed for every k, so DFT is O(N2)
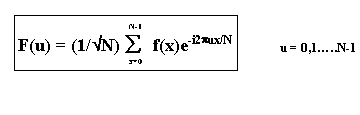 F(u) = DFT of f(x)
N = number of input samples
x = dummy variable used to index the sample
1/N1/2 = Normalize the spectrum WRT input length
F(u) = DFT of f(x)
N = number of input samples
x = dummy variable used to index the sample
1/N1/2 = Normalize the spectrum WRT input length
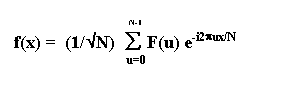
f(x) is a reconstruction from the integral harmonic of fs/N
Sun Au files
as read by the Java API
fs = 8000 Hz
N = 8000 sample
Thus available Reconstruction harmonic are :
fs / N = 8000/8000 = 1,2...4KHz
fs / N = 8000/800 = ± 10,± 20....± 4KHz
Negative frequencies Occupy the N/2à.N-1 position in the DFT and have no physical meaning.
The maximum allowable f is 1/2 fs
fs = 8000 Hz
fmax = 4000 Hz
k E [ 0...N/2 ]
fs/N = 10
N = 400
Card { 10 20 30....200 } = 20
The 2D Fourier Transform :
Let f(x,y) it is continuous and integrable
The
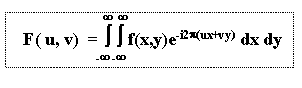
u and v are in the frequency domain
The Fourier spectrum
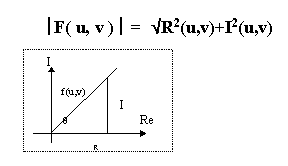
The phase
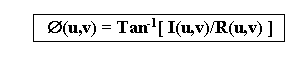
In 2-D the DFT
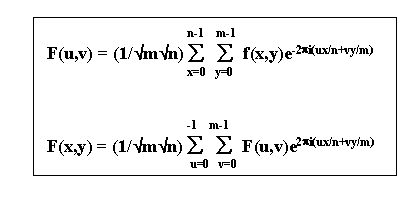
u, x = 0,...n-1
x, y = 0,... m-1
 Last
Update: 04/09/97
Last
Update: 04/09/97
Copyright © 1997- Douglas Lyon
Lyon@cse.bridgeport.edu