![]()
Lecture Topics:
int bitr(int j) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i< nu; i++) {
ans = (ans <<1) + (j&1);
j = j>>1;
}
return ans;
}
public void swap(int i) {
double tempr;
int j = bitr(i);
String js = Integer.toBinaryString(j);
String is = Integer.toBinaryString(i);
//System.out.println("swap "+is+","+js);
// System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i)+"bitr="+Integer.toBinaryString(bitr(i)));
tempr = r_data[j];
r_data[j] = r_data[i];
r_data[i] = tempr;
tempr = i_data[j];
i_data[j] = i_data[i];
i_data[i] = tempr;
}
void swap(i,j){i = i^j; j = i^j; i = i^j;}

fs = Sample Rate
= amount of time your wave table will play.

public void sawWave() {
// The number of cycles per second is
double frequency = 440.0;
//
// Three partial summations of sine waves to
// make a sawtooth wave approximation
// These three forms show the harmonic
// content of a sawtooth wave.
//
doubleData = new double[8000];
// f = 1/(waveLength/8000);
// waveLength/ 8000 = 1/f
// waveLength = 8000/f
// waveLength = (int)( 1+ 2/step )
// (waveLength - 1)* step = 2
// step = 2/(waveLength)
// step = 2/(8000/f) = 2*f/8000 = f/4000;
// and it sounds flat!
// I wonder if it is being resampled at the 8125 rate.
double sample_rate = 8125.;
double step = frequency/(sample_rate/2);
int waveLength = (int)( 2/step );
int i = 0;
int number_of_waves = 1 + doubleData.length / waveLength;
do
done: for (double n = -1; n < 1; n = n + step) {
doubleData[i] = n;
i++;
if (i >= doubleData.length) { break done;}
}
while (i < doubleData.length);
ulawData=Audio.encodeUlaw(doubleData);
audioDataStream = new AudioDataStream(new AudioData(ulawData));
play();
}
ulawDate = Audio.encodeulaw(doubleDate); audioDataStream = new AudioDataStream( new AudioData( ulawData ) ); play( );
Byte ulaw.to-ulaw( double d )
public void sineWave() {
int length = 16;
ulawData = new byte[length];
double t = 0;
// The number of cycles per second is
double frequency = 440.0;
double dt = delta_t();
// t will range from 0.. delta_t * length
// Assume that there are 8k samples/second
// Then the waveform will clock out
// it will also clock out 8000/length times per second
// so, if you want the wave form to clock out at
// 440 hz, then 8000/length = 440, and length = 8000/440
// = 18 bytes.. If length = 8000, then you need
// 440 cycles from 0..2*pi
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
ulawData[i] = Ulaw.to_ulaw(sin(pi_2 *t));
t = t + dt;
}
audioDataStream = new AudioDataStream(new AudioData(ulawData));
play();
}

public void triangleWave() {
// The number of cycles per second is
double frequency = 880.0;
//
doubleData = new double[8000];
// f = 1/(waveLength/8000);
// waveLength/ 8000 = 1/f
// waveLength = 8000/f
// waveLength = (int)( 1+ 2/step )
// (waveLength - 1)* step = 2
// step = 2/(waveLength)
// step = 2/(8000/f) = 2*f/8000 = f/4000;
double sample_rate = 8125.;
double step = frequency/(sample_rate/2);
int waveLength = (int)( 2/step );
int i = 0;
int number_of_waves = 1 + doubleData.length / waveLength;
do
{
done: for (double n = -1; n < 1; n = n + step) {
doubleData[i] = n;
i++;
if (i >= doubleData.length)
{ break done;}
}
// Do second half of triangle only if there is room.
// Simply use same type of loop to generate triangle
// wave as used for saw tooth wave.
if (i < doubleData.length) {
done2: for (double n = 1; n > -1; n = n - step) {
doubleData[i] = n;
i++;
if (i >= doubleData.length)
{ break done2;}
}
}
}
while (i < doubleData.length);
ulawData=Audio.encodeUlaw(doubleData);
audioDataStream = new AudioDataStream(new AudioData(ulawData));
play();
}

via, the principle of superposition





-sin( x ) = sin( x )
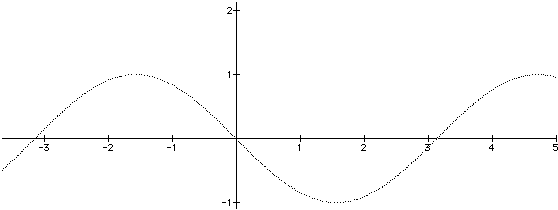
Sine is an odd function
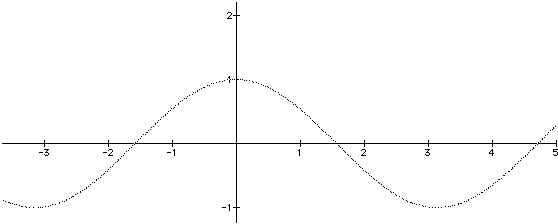
Cosine is an even function
f( -x ) = f( x ) implies f is an even function
 Last Update:
04/09/97
Last Update:
04/09/97