![]()
Lecture Topics:
![]()
The 1-D Fourier Series
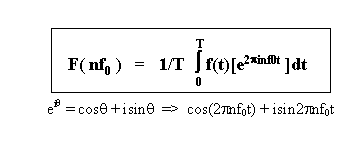
f0 = 1/T
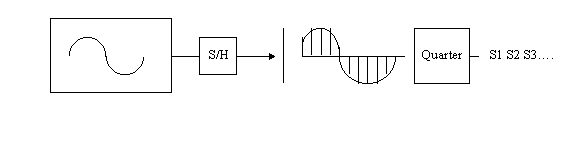
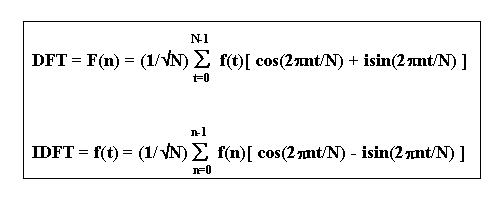
Summary : f( t ) is sampled and assumed periodic over the N sampled points
Max positive fmax = n = N/2
2-D the DFT
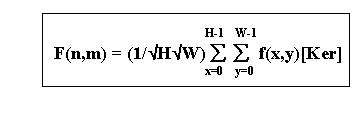
Ker = [ cos(2p nx/W) + isin(2p nx/W) ] * Kery
Kery = [ cos(2p my/H) + isin(2p my/H) ]
Forward Fourier( float f[], float f1[], float far[], float fQi[] ) {
p=math.PI; for( int n=0; n<Ö
o/p = FFT(i);
float[][] fft(float I[][]){Ö.}
PB = P&xFF PG = (P>>8)&xFF PR = (P>>16)&xFF PA = (P>>2)&xFF
P= | A | R | G | B | => 32 bits float = 32 bits double = 64 bits
Benchmarking in Java
* Time class
API - Time t = new Time(); methodsclear(); start(); stop(); get_time(); return elapsed time in seconds.
Timer.java
import java.io.*; public class Timer { private long base_time; private long elapsed_time; private static final long UNIT = 1000; public Timer() { clear(); } public void mark() { base_time = System.currentTimeMillis(); } public void clear() { elapsed_time = 0; } public void record() { elapsed_time += (System.currentTimeMillis() - base_time); } public float elapsed() { return ((float) elapsed_time) / UNIT; } public void report(PrintStream pstream) { float elapsed_seconds = elapsed(); pstream.println("Time " + elapsed_seconds + " sec"); } public void report() { report(System.out); } }
Danielson-Lanczos
DFT O(N2)
complex multiplications
D&L break down into 2 DFTís
each of length N/2
One is even sample, other is odd sample.
Proof
wjk = e2p ijk/N
if j = 0,1,2,3Ö.
2j = 0,2,4,6Ö.
2j+1= 1,3,5,7Ö.
Decimation in time:
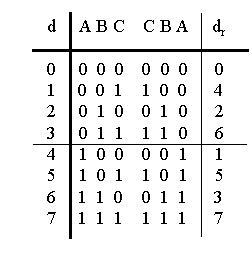
N = 8
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
{0, 2, 4, 6} { 1, 3, 5, 7}
{0, 4} {2, 6} {1, 5} {3, 7}
static final short[] bit_Ar{ NoÖ, Ö.No65535 }
int bit R(int i){short i1 = i&xFFFF; short i2 = (I>>16)&xFFFF; i1= bit_Ar[i1]; i2 = bit_Ar[i2]; return (( i1<<16) + i2);}
 Last Update:
04/09/97
Last Update:
04/09/97
Copyright © 1997- Douglas Lyon
Lyon@cse.bridgeport.edu